Step :1
Open terminal using command Ctrl+T.
Step 2:
Update your existing list of packages.
Step 3:
Install prerequisite packages which let apt use packages over HTTPS:
Step 4:
Add GPG key for the official Docker repository to your system:
Step 5:
Add the Docker repository to APT sources:
Step 6:
Update the package database
Step 7:
Make sure you are about to install from the Docker repo instead of the default Ubuntu repo:
You'll see output like this, although the version number for Docker may be different:
Notice that docker-ce is not installed
Step 8:
Finally, install Docker:
Step 9:
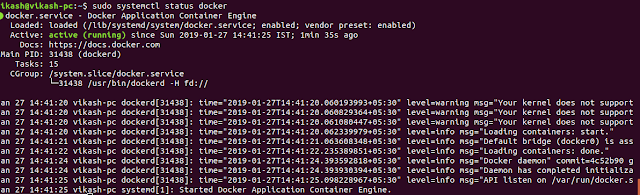
Docker should now be installed, the daemon started, and the process enabled to start on boot. Check that it's running:
Installing Docker now gives you not just the Docker service (daemon) but also the docker command line utility,
Step 10:
To view system-wide information about Docker, use:

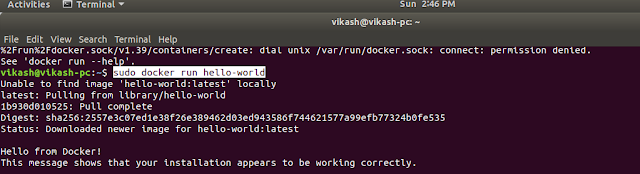
To check whether you can access and download images from Docker Hub, type:
Step 11:
To see the images that have been downloaded to your computer, type:

The output should look similar to the following:
The hello-world container you ran in the previous step is an example of a container that runs and exits after emitting a test message. Containers can be much more useful than that, and they can be interactive.
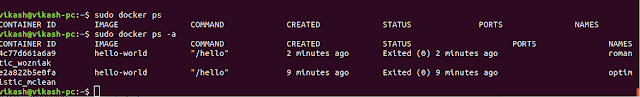
After using Docker for a while, you'll have many active (running) and inactive containers on your computer. To view the active ones, use:
check latest one

To view all containers — active and inactive, run docker ps with the -a switch:
Thats all in terms of installing Docker and some basic commands.
Open terminal using command Ctrl+T.
Step 2:
Update your existing list of packages.
sudo apt update
Step 3:
Install prerequisite packages which let apt use packages over HTTPS:
sudo apt install apt-transport-https ca-certificates curl software-properties-common
Step 4:
Add GPG key for the official Docker repository to your system:
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo apt-key add -
Step 5:
Add the Docker repository to APT sources:
sudo add-apt-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu bioni
Step 6:
sudo apt update
Step 7:
apt-cache policy docker-ce
You'll see output like this, although the version number for Docker may be different:
Notice that docker-ce is not installed
Step 8:
sudo apt install docker-ce
Step 9:
sudo systemctl status docker

Installing Docker now gives you not just the Docker service (daemon) but also the docker command line utility,
Step 10:
docker info
This will give you permission error so try with sudo you can check more on how to avoid using sudo everytime
sudo docker info
To check whether you can access and download images from Docker Hub, type:
Step 11:
sudo docker run hello-world

To see the images that have been downloaded to your computer, type:
sudo docker images
The output should look similar to the following:
The hello-world container you ran in the previous step is an example of a container that runs and exits after emitting a test message. Containers can be much more useful than that, and they can be interactive.
After using Docker for a while, you'll have many active (running) and inactive containers on your computer. To view the active ones, use:
sudo docker ps

check latest one
sudo docker ps -l
To view all containers — active and inactive, run docker ps with the -a switch:
sudo docker ps -a
Thats all in terms of installing Docker and some basic commands.


Comments
Post a Comment